🧬 What Is Transgenics ?
Transgenics refers to the field of biotechnology in which the genetic material of an organism is deliberately modified to include DNA from a different species, strain, or breed. This process is achieved through genetic engineering techniques and is used widely in modern research, medicine, and biotechnology.

🧬 Transgenics Defined
Transgenics is most commonly defined as:
- An organism that contains genetic material into which DNA from an unrelated organism has been artificially introduced.
- A biological system in which foreign genes or DNA sequences are integrated into all cells of an organism via genetic engineering methods.
- A living being whose genome has been altered to include one or more genes transferred from another species or lineage.
These definitions underscore the cross-species genetic transfer at the core of transgenic research and technology.

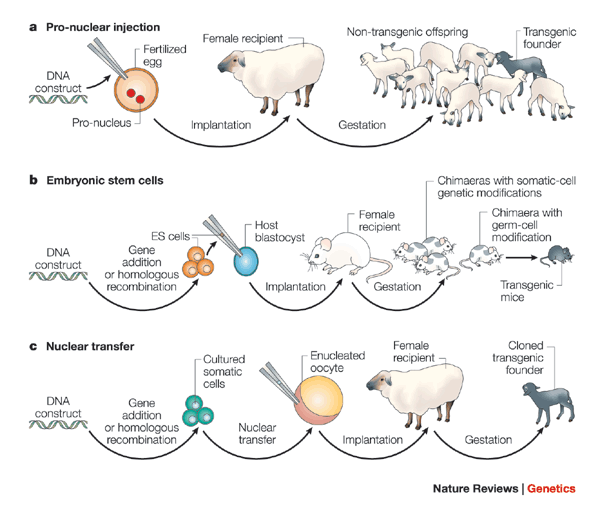
🐭 What Is a Transgenic Animal?
A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been deliberately modified to carry foreign DNA that becomes part of its heritable genetic material. The foreign gene is introduced into the animal's germ line, ensuring that every cell—somatic and germinal—contains the same modified genetic sequence. Transgenic animals are widely used in:
- Biomedical research
- Disease modeling (e.g., Alzheimer's, cancer, autoimmune diseases)
- Therapeutic protein production (e.g., monoclonal antibodies)
- Functional gene studies and pharmacogenomics
🧬 How Do Transgenics Differ from Chimeras?
A chimera is not the same as a transgenic animal. While a transgenic animal has the same foreign DNA in every cell, a chimeric animal contains cells from two or more genetically distinct embryos. These can be:
- Intra-specific chimeras: formed from embryos of the same species
- Inter-specific chimeras: formed from embryos of different species
Chimeric embryos are created by injecting foreign cells into an early-stage host embryo. These cells integrate and contribute to the development of different tissues or organs.

🔬 Relevance of Transgenics in Modern Biology
Transgenics plays a critical role in modern biological research, with applications including:
- Gene function analysis
- Disease modeling in animals
- Pharmaceutical biomanufacturing
- Agricultural trait enhancement
- Vaccine development and antibody generation